
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, Engineering Research Center of Optical Instrument and System (Ministry of Education), School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Chongqing Key Laboratory of Precision Optics, Chongqing Institute of East China Normal University, Chongqing 401120, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
4 e-mail: qwzhan@usst.edu.cn
In this study, we present a method for free-space beam shaping and steering based on a silicon optical phased array, which addresses the theoretical limitation of traditional bulk optics. We theoretically analyze the beam propagation properties with changes in the applied phase. Different beam profiles can be shaped by varying the phase combination, while a high-order quasi-Bessel beam can be generated with a cubic change to the phase modulation. The simulated results are validated further experimentally, and they match one another well. Beam steering can be achieved with a field of view as large as 140°, which has potential benefits for practical applications. The presented method is expected to have broad application prospects for optical communications, free-space optical interconnects, and light detection and ranging.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(12): 2093
上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
随着激光技术的迅猛发展,超快光学已经成为现代物理学研究中一个非常重要的前沿领域。高次谐波作为产生超短激光脉冲的重要手段之一,在近十年内快速发展。本文综述了气体高次谐波产生过程中存在的自旋角动量守恒、轨道角动量守恒、自旋-轨道相互作用以及由此引出的新奇物理现象,总结了现阶段研究所存在的部分空白与挑战。将结构光场应用于高次谐波领域极大地丰富了人们研究光与物质相互作用的手段,为光学操控和强场物理带来了新的机遇。
物理光学 谐波产生与混频 强场过程 超快非线性光学 角动量守恒 自旋-轨道相互作用 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(15): 1526001
上海理工大学 光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
一定强度的飞秒激光聚焦于空气能生成空气等离子体并诱导生成冲击波。为了观察该冲击波传播特性,引入了超快时间分辨涡旋滤波成像技术,并对观测到的冲击波动力学过程进行了分析。实验探测到泵浦能量为1.5 mJ的飞秒激光经过透镜聚焦到空气中产生等离子体空气冲击波,分析了在3~15 μs时间段冲击波的动态演化过程。结果表明,飞秒激光等离子体空气冲击波在传输时以不对称的球形形状向外扩散,且沿着激光传播方向的传播速度与背着激光传播方向的传播速度不同,分别为372 m/s和341 m/s。这一观察结果与传统的点爆炸模型的对称情形不同,尝试对该不对称动力学过程进行了合理解释。
超快时间分辨成像 涡旋滤波 空气等离子体 冲击波 ultrafast time-resolved vortex filter air plasma shock wave 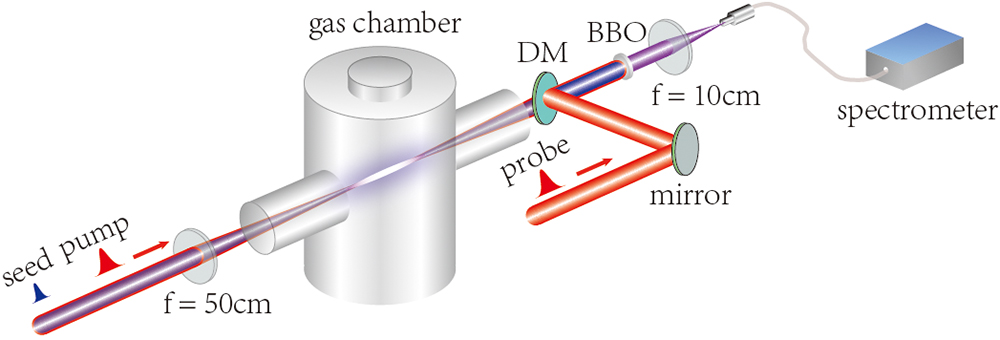
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
We experimentally investigated the forward 353.8 nm radiation from plasma filaments in pure nitrogen gas pumped by intense circularly polarized 800 nm femtosecond laser pulses. This emission line corresponds to the transition of nitrogen ions. In the presence of an external seeding pulse, the 353.8 nm signal was amplified by 3 orders of magnitude. Thanks to the much enhanced intensity, we performed time-resolved measurement of the amplified 353.8 nm emission based on the sum-frequency generation technique. It was revealed that the built-up time and duration of these emissions are both inversely proportional to the gas pressure, while the radiation peak power grows up nearly quadratically with pressure, indicating that the 353.8 nm radiation is of the nature of superradiance.
femtosecond pulses plasma nitrogen ions superradiance time-resolved measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 023201





